Benchmark Apps For Mac
Jun 07, 2019 10 Best Benchmark Apps to Measure Your Mac’s Performance 1. Disk Speed Test. UNIQUE Benchmarks. Phoronix Test Suite. Tyler’s Frame Machine. Aug 22, 2019 There are tools available to measure Mac SSD performance and monitor SSD life. We listed best SSD Tools for MAC to Maintain SSD Drive. This app supports modern SSDs and HDDs and offers real-time SSD/HDD health status monitoring. It can display SSD lifetime left indicator, save drive’s health report to file and monitor drive temperature. What are good benchmarks for a Mac Geekbench muilti-core: 31,066. Cinebench R20: 3,222. Unigine Valley: 3,369. May 31, 2016 Love it, a real disk benchmark app for osx One thing that was always missing since I moved from windows 5 years back was a speed test app for my external harddrives. Although there were other apps I tried, most would just be a jazzy interface that gave highly inaccurate results. Over the following years, Alfred Scott and Jim Petty developed Benchmark as a computer program to automate the entire process, beginning with a very basic program that ran on the early Mac Plus in 1990. Once the data was entered, Benchmark would do all the calculations required for engine power, propeller efficiency, airplane speed.
- Benchmarks For Mac
- Best Benchmark Tool For Mac
- Mac Performance Check
- Benchmark App For Mac
- Cool Apps For Mac
- Game Apps For Mac
This article describes some of the commonly used features of Activity Monitor, a kind of task manager that allows you see how apps and other processes are affecting your CPU, memory, energy, disk, and network usage.
Open Activity Monitor from the Utilities folder of your Applications folder, or use Spotlight to find it.
Overview
The processes shown in Activity Monitor can be user apps, system apps used by macOS, or invisible background processes. Use the five category tabs at the top of the Activity Monitor window to see how processes are affecting your Mac in each category.
Add or remove columns in each of these panes by choosing View > Columns from the menu bar. The View menu also allows you to choose which processes are shown in each pane:
- All Processes
- All Processes Hierarchically: Processes that belong to other processes, so you can see the parent/child relationship between them.
- My Processes: Processes owned by your macOS user account.
- System Processes: Processes owned by macOS.
- Other User Processes: Processes that aren’t owned by the root user or current user.
- Active Processes: Running processes that aren’t sleeping.
- Inactive Processes: Running processes that are sleeping.
- Windowed Processes: Processes that can create a window. These are usually apps.
- Selected Processes: Processes that you selected in the Activity Monitor window.
- Applications in the last 8 hours: Apps that were running processes in the last 8 hours.
CPU
Benchmarks For Mac
The CPU pane shows how processes are affecting CPU (processor) activity:
Click the top of the “% CPU” column to sort by the percentage of CPU capability used by each process. This information and the information in the Energy pane can help identify processes that are affecting Mac performance, battery runtime, temperature, and fan activity.
More information is available at the bottom of the CPU pane:
- System: The percentage of CPU capability currently used by system processes, which are processes that belong to macOS.
- User: The percentage of CPU capability currently used by apps that you opened, or by the processes those apps opened.
- Idle: The percentage of CPU capability not being used.
- CPU Load: The percentage of CPU capability currently used by all System and User processes. The graph moves from right to left and updates at the intervals set in View > Update Frequency. The color blue shows the percentage of total CPU capability currently used by user processes. The color red shows the percentage of total CPU capability currently used by system processes.
- Threads: The total number of threads used by all processes combined.
- Processes: The total number of processes currently running.
You can also see CPU or GPU usage in a separate window or in the Dock:
- To open a window showing current processor activity, choose Window > CPU Usage. To show a graph of this information in your Dock, choose View > Dock Icon > Show CPU Usage.
- To open a window showing recent processor activity, choose Window > CPU History. To show a graph of this information in your Dock, choose View > Dock Icon > Show CPU History.
- To open a window showing recent graphics processor (GPU) activity, choose Window > GPU History. Energy usage related to such activity is incorporated into the energy-impact measurements in the Energy tab of Activity Monitor.
Memory
The Memory pane shows information about how memory is being used:
Best Benchmark Tool For Mac
More information is available at the bottom of the Memory pane:
- Memory Pressure: The Memory Pressure graph helps illustrate the availability of memory resources. The graph moves from right to left and updates at the intervals set in View > Update Frequency. The current state of memory resources is indicated by the color at the right side of the graph:
- Green: Memory resources are available.
- Yellow: Memory resources are still available but are being tasked by memory-management processes, such as compression.
- Red: Memory resources are depleted, and macOS is using your startup drive for memory. To make more RAM available, you can quit one or more apps or install more RAM. This is the most important indicator that your Mac may need more RAM.
- Physical Memory: The amount of RAM installed in your Mac.
- Memory Used: The total amount of memory currently used by all apps and macOS processes.
- App Memory: The total amount of memory currently used by apps and their processes.
- Wired Memory: Memory that can’t be compressed or paged out to your startup drive, so it must stay in RAM. The wired memory used by a process can’t be borrowed by other processes. The amount of wired memory used by an app is determined by the app's programmer.
- Compressed: The amount of memory in RAM that is compressed to make more RAM memory available to other processes. Look in the Compressed Mem column to see the amount of memory compressed for each process.
- Swap Used: The space used on your startup drive by macOS memory management. It's normal to see some activity here. As long as memory pressure is not in the red state, macOS has memory resources available.
- Cached Files: Memory that was recently used by apps and is now available for use by other apps. For example, if you've been using Mail and then quit Mail, the RAM that Mail was using becomes part of the memory used by cached files, which then becomes available to other apps. If you open Mail again before its cached-files memory is used (overwritten) by another app, Mail opens more quickly because that memory is quickly converted back to app memory without having to load its contents from your startup drive.
For more information about memory management, refer to the Apple Developer website.
Energy
The Energy pane shows overall energy use and the energy used by each app:
- Energy Impact: A relative measure of the current energy consumption of the app. Lower numbers are better. A triangle to the left of an app's name means that the app consists of multiple processes. Click the triangle to see details about each process.
- Avg Energy Impact: The average energy impact for the past 8 hours or since the Mac started up, whichever is shorter. Average energy impact is also shown for apps that were running during that time, but have since been quit. The names of those apps are dimmed.
- App Nap: Apps that support App Nap consume very little energy when they are open but not being used. For example, an app might nap when it's hidden behind other windows, or when it's open in a space that you aren't currently viewing.
- Preventing Sleep: Indicates whether the app is preventing your Mac from going to sleep.
More information is available at the bottom of the Energy pane:

- Energy Impact: A relative measure of the total energy used by all apps. The graph moves from right to left and updates at the intervals set in View > Update Frequency.
- Graphics Card: The type of graphics card currently used. Higher–performance cards use more energy. Macs that support automatic graphics switching save power by using integrated graphics. They switch to a higher-performance graphics chip only when an app needs it. 'Integrated' means the Mac is currently using integrated graphics. 'High Perf.' means the Mac is currently using high-performance graphics. To identify apps that are using high-performance graphics, look for apps that show 'Yes' in the Requires High Perf GPU column.
- Remaining Charge: The percentage of charge remaining on the battery of a portable Mac.
- Time Until Full: The amount of time your portable Mac must be plugged into an AC power outlet to become fully charged.
- Time on AC: The time elapsed since your portable Mac was plugged into an AC power outlet.
- Time Remaining: The estimated amount of battery time remaining on your portable Mac.
- Time on Battery: The time elapsed since your portable Mac was unplugged from AC power.
- Battery (Last 12 hours): The battery charge level of your portable Mac over the last 12 hours. The color green shows times when the Mac was getting power from a power adapter.
As energy use increases, the length of time that a Mac can operate on battery power decreases. If the battery life of your portable Mac is shorter than usual, you can use the Avg Energy Impact column to find apps that have been using the most energy recently. Quit those apps if you don't need them, or contact the developer of the app if you notice that the app's energy use remains high even when the app doesn't appear to be doing anything.
Disk
The Disk pane shows the amount of data that each process has read from your disk and written to your disk. It also shows 'reads in' and 'writes out' (IO), which is the number of times that your Mac accesses the disk to read and write data.
The information at the bottom of the Disk pane shows total disk activity across all processes. The graph moves from right to left and updates at the intervals set in View > Update Frequency. The graph also includes a pop-up menu to switch between showing IO or data as a unit of measurement. The color blue shows either the number of reads per second or the amount of data read per second. The color red shows either the number of writes out per second or the amount of data written per second.
To show a graph of disk activity in your Dock, choose View > Dock Icon > Show Disk Activity.
Network
The Network pane shows how much data your Mac is sending or receiving over your network. Use this information to identify which processes are sending or receiving the most data.
The information at the bottom of the Network pane shows total network activity across all apps. The graph moves from right to left and updates at the intervals set in View > Update Frequency. The graph also includes a pop-up menu to switch between showing packets or data as a unit of measurement. The color blue shows either the number of packets received per second or the amount of data received per second. The color red shows either the number of packets sent per second or the amount of data sent per second.
To show a graph of network usage in your Dock, choose View > Dock Icon > Show Network Usage.
Cache
In macOS High Sierra 10.13.4 or later, Activity Monitor shows the Cache pane when Content Caching is enabled in the Sharing pane of System Preferences. The Cache pane shows how much cached content that local networked devices have uploaded, downloaded, or dropped over time.
Use the Maximum Cache Pressure information to learn whether to adjust Content Caching settings to provide more disk space to the cache. Lower cache pressure is better. Learn more about cache activity.
Mac Performance Check
The graph at the bottom shows total caching activity over time. Choose from the pop-up menu above the graph to change the interval: last hour, 24 hours, 7 days, or 30 days.
Learn more
- Learn about kernel task and why Activity Monitor might show that it's using a large percentage of your CPU.
- For more information about Activity Monitor, open Activity Monitor and choose Help > Activity Monitor. You can also see a short description of many items in the Activity Monitor window by hovering the mouse pointer over the item.
We all know Macs are quite durable machines that tend to last for years. Naturally, their performance starts lagging at some point, but for a long time, it’s barely noticeable. So how do we know it’s time for a change and our Macs are a bit behind the current industry standard? Benchmark apps!
Benchmark apps and utilities that help you measure your Mac’s performance against a variety of user benchmarks set by top computers in production at the moment. Knowing how your Mac fares against its alternatives helps you better evaluate its capabilities when it comes to projecting what you’ll need it for in the future. In addition, you can also perform a benchmark test on a Mac you’re planning to buy to see if the purchase makes sense for you.
What Are The Most Common Mac Benchmarks?
While userbenchmarks are great, what exactly do they measure? In general, there are six common metrics: a CPU speed test, a RAM speed test, a GPU benchmark test, a network connection test, and a disk speed test Macs use to check how long it takes for information to be written on and read from your hard drives.
Here are the five best apps to help you perform Mac speed tests quickly and effectively.
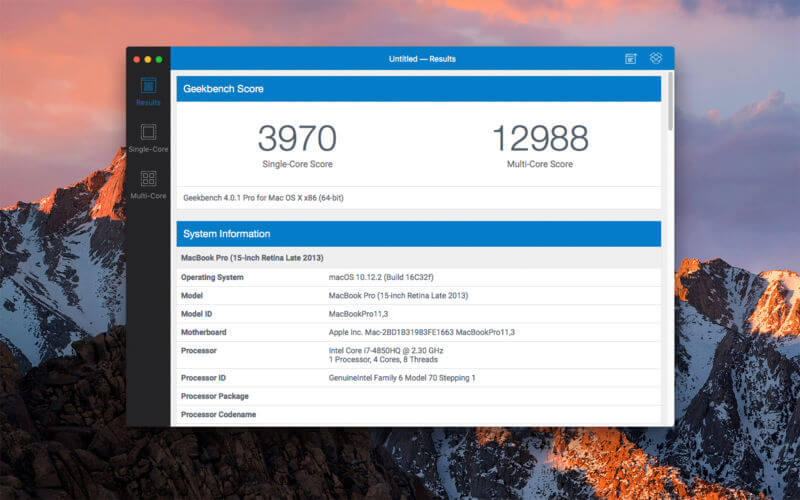
1. Conduct CPU and GPU tests with Geekbench Mac
CPU and GPU benchmarks are probably what everyone immediately assumes when someone mentions Mac speed tests. CPU stands for central processing unit and is basically represented by a chip in your Mac, such as Intel Core i7, for example. GPU then is a graphics processing unit — your video card, responsible for how quickly and accurately your Mac is able to display everything. If there’s one app that excels at both benchmark CPU and GPU tests, it’s Geekbench.
Geekbench is a cross-platform (Mac, Linux, Windows) GPU and CPU test utility that measures the performance of your Mac against a widely publicized and well-known standard. For Geekbench 5, the latest version, the passmark CPU was 1,000, as performed by an Intel Core i3-8100 chip.
Starting with Geekbench couldn’t be easier:
Processor: Intel Core i5 or better. Video: NVIDIA GeForce 750M or AMD Radeon R9 M290X. Warcraft 3 frozen throne for mac free download. Operating System: macOS 10.13 (latest version).
Download the app from the App Store (costs around $9.99)
Launch and check the Device tab to make sure your Mac’s info is correct
For benchmark CPU tests, go to the CPU tab and click Run CPU Benchmark
For benchmark GPU tests, select Run Compute Benchmark in the Compute tab
Now you can always be aware of how your Mac performance and potentially think about various tactics to improve it (closing Safari tabs, using fewer apps, etc.) or replacing it altogether.
2. Check you hard drives with Blackmagic
The second most important parameter after CPU and GPU benchmarks is the hard drive speed test Macs can perform with the help of Blackmagic disk speed test Mac utility.
Blackmagic is as straightforward of an app as possible, with only one large interface button — Speed Test Start. Simply press the button to calculate your userbenchmark score based on the performance of your hard drives. Done!
Benchmark App For Mac
Make sure to undergo the tests regularly (once a quarter or so) to consider swapping your storage disks when they get too slow.
3. Manage your network with WiFi Explorer
Another crucial Mac performance test, especially since nearly all our work today takes place online, is measuring the efficacy of your network. After all, maybe it’s not your MacBook that should be replaced but your WiFi provider?
WiFi Explorer is exactly the app you need to see how good your internet connection really is. It clearly maps out the strength of your signal, displays signal quality, and calculates the level of interference.
Anytime you think your WiFi has been underperforming, just turn on WiFi Explorer and it’ll start to do its job automatically (press the play icon if not). Then you have the precise information to tell your ISP and get them to fix it or agree on a discount (hopefully), or both.
Cool Apps For Mac
4. See all metrics in real time with iStat Menus
By now, you might wonder whether there is an easier solution than having Geekbench, Blackmagic, and WiFi Explorer constantly turned on? While WiFi Explorer is quite important and can only be used when you notice a connection problem, Geekbench and Blackmagic could certainly be replaced by a single powerful system monitor called iStat Menus.
iStat Menus is one of the most comprehensive and unobtrusive Mac monitors on the market today. This utility lives in your menu bar and gives you a complete overview of what’s going on with your processor, graphics card, hard drives, memory, and various sensors.
Game Apps For Mac
Unlike many other GPU and CPU benchmark tools, iStat Menus provides you with a real-time picture of what’s going on, so you can react to any issues as soon as they come up or see the dip in performance over time more clearly. All the best Mac performance tests in one!
5. Improve benchmark tests with CleanMyMac X
When iStat Menus is giving you clear indicators of user benchmarks not being reached, what do you do? Of course you can run to the Apple Store and buy a new Mac, but a more sensible (and inexpensive!) solution would be to try to fix the problem with a good optimization tool.
CleanMyMac X is often regarded as the best optimization app on the market, able to perform a variety of tests to free up RAM, speed up your hard drives, clear useless cache files, and smoothen your Mac’s performance overall.
Let’s walk through a few CleanMyMac X tests for a real-life example of its possibilities. Start with a general system cleanup to act on your CPU speed test:
Navigate to the System Junk tab and hit Scan
Click Review Details
Check all log files, login items, downloads, and more, and press Clean
But that’s not all, CleanMyMac X also offers you a simple way to improve your Mac benchmarks in memory:
Go to the Maintenance tab, under Speed
Check the box next to Free Up RAM
Hit Run
With this quick script, all the unused bits of memory have been collected together, ready for you to throw more tasks their way. As for your hard drives, consider activating two more scripts:
Make sure you’re in the same Maintenance tab
Select Free Up Purgeable Space and Repair Disk Permissions
Click Run
Just like that your CPU, GPU, RAM, and hard drives should now feel brand new and lightning fast. This is how monitoring all aspects of your Mac using WiFi Explorer and iStat Menus can lead to actual improvements made by CleanMyMac X.
Best of all, WiFi Explorer, iStat Menus, and CleanMyMac X are available to you free during a seven-day trial of Setapp, a platform with more than 160 top-notch Mac apps that can help you with almost any task imaginable. And now that your Mac is super quick, why not explore some new ideas?